One of the neat features ZFS offers is the ability to create a filesystem from a file. This is especially useful when a secure or portable filesystem needs to be created.
I often use this method to create a small, secure ZFS volume that I can later move to another system by simply copying the underlying file.
Creating a pool
First, I recommend creating a separate directory for the pool files:
mkdir /path/to/zfs-pool-something
Next, create a file to represent the virtual block device. There are at least two ways to do this:
truncate -s 256M /path/to/zfs-pool-something/zfs-pool-something-1dd if=/dev/zero of=/path/to/zfs-pool-something/zfs-pool-something-1 bs=1M count=256
In both examples, the file size is set to 256 megabytes.
The difference between the tools is:
-
truncateinstantly creates a sparse file. The file takes up almost no physical disk space until you start writing data to it. -
ddcreates a fully allocated file, the file is filled with zeroes and takes physical disk space.
Finally, create the pool using the file:
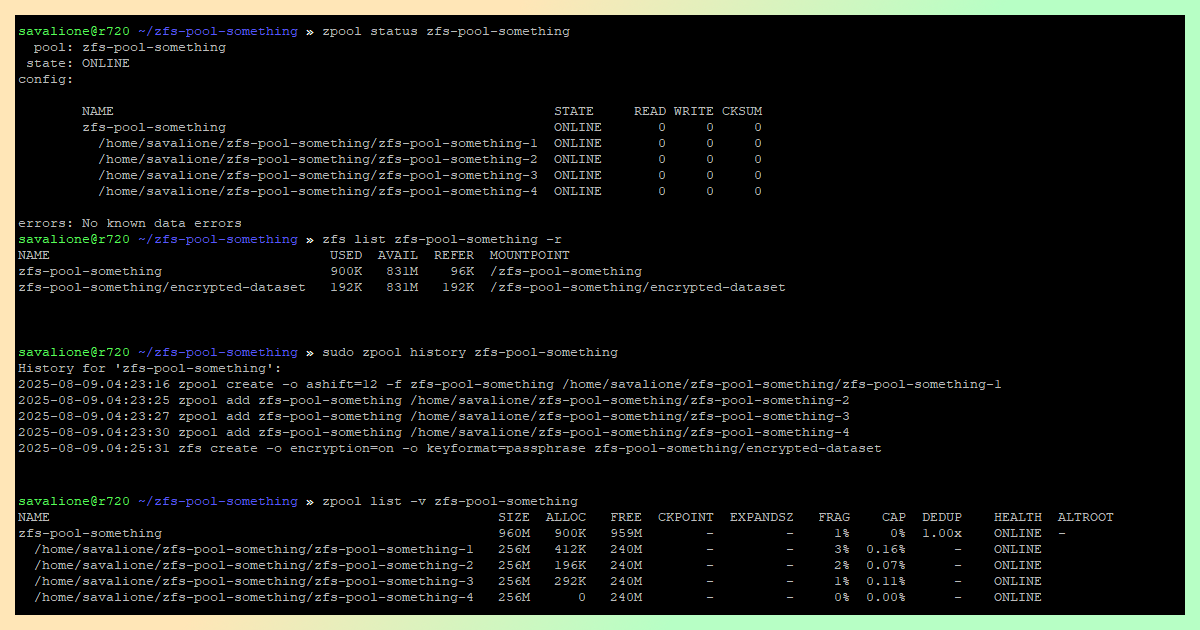
sudo zpool create -o ashift=12 -f zfs-pool-something /path/to/zfs-pool-something-1
Importing a pool
To import the pool on another system (or after an export), you need to specify the pool’s name and the directory containing its files:
sudo zpool import -d /path/to/zfs-pool-something zfs-pool-something
Exporting a pool
Exporting the pool works the same as with any other ZFS pool:
sudo zpool export zfs-pool-something
Expanding a pool
To expand a pool, you have several options. Here are two common methods:
- Add a new file to the pool, expanding its total capacity.
- Replace an existing file with a larger one.
Method 1: Add a new file to the pool
This it the method I usually use and is the simplest.
- Create a new, larger file:
truncate -s 512M /path/to/zfs-pool-something/zfs-pool-something-2
- Add the new file to the pool:
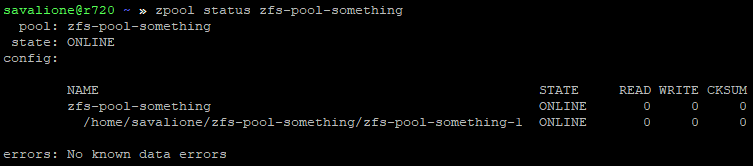
sudo zpool add zfs-pool-something /path/to/zfs-pool-something/zfs-pool-something-2
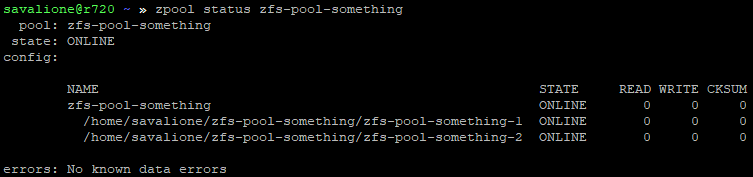
The pool’s total capacity will now be the sum of both files (256mb + 512mb - ZFS metadata).
Method 2: Replacing an existing file with a new one
This method is useful for keeping the number of underlying files constant.
- Create a new, larger file:
truncate -s 512M /path/to/zfs-pool-something/zfs-pool-something-2
- Tell ZFS to replace the old file with the new one:
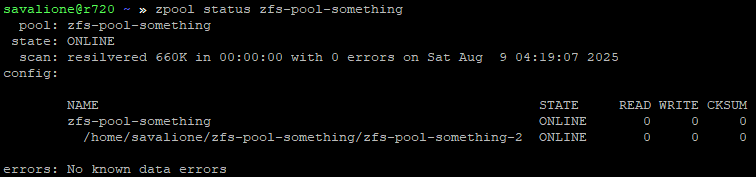
sudo zpool replace zfs-pool-something /path/to/zfs-pool-something/zfs-pool-something-1 /path/to/zfs-pool-something/zfs-pool-something-2
Once ZFS has moved the data in the background (resilvering), the old file can be deleted.
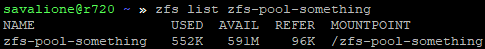
Creating an encrypted dataset
After creating the pool, you can easily add a native ZFS encrypted dataset:
sudo zfs create -o encryption=on -o keyformat=passphrase zfs-pool-something/encrypted-dataset
This dataset and any data within it will now be encrypted.
Changelog
- 2025-08-09: Corrected grammar and added images.